11. Quiz: JOIN Questions Part I
Question Mania
Now that you have been introduced to JOINs, let's practice to build your skills and comfort with this new tool. Below I have provided the ERD and a bunch of questions. The solutions for the questions can be found on the next concept for you to check your answers or just in case you get stuck!
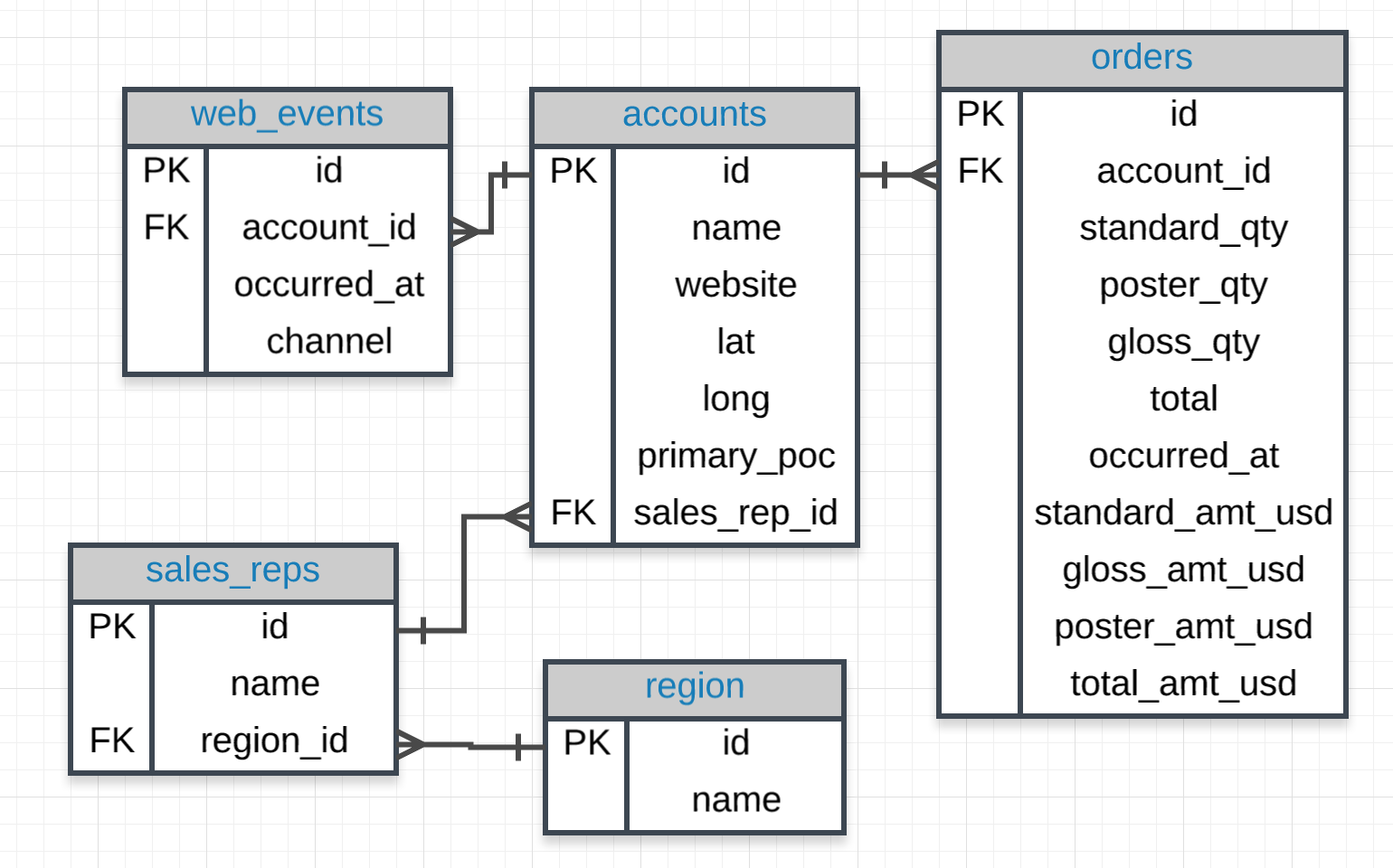
I recommend testing your queries with the environment below, and then saving them to a file. Then compare your file to my solutions on the next concept!
Questions
- Provide a table for all web_events associated with account name of
Walmart. There should be three columns. Be sure to include theprimary_poc, time of the event, and thechannelfor each event. Additionally, you might choose to add a fourth column to assure onlyWalmartevents were chosen. - Provide a table that provides the region for each sales_rep along with their associated accounts. Your final table should include three columns: the region name, the sales rep name, and the account name. Sort the accounts alphabetically (A-Z) according to account name.
- Provide the name for each region for every order, as well as the account name and the unit price they paid (total_amt_usd/total) for the order. Your final table should have 3 columns: region name, account name, and unit price. A few accounts have 0 for total, so I divided by (total + 0.01) to assure not dividing by zero.
Workspace
This section contains either a workspace (it can be a Jupyter Notebook workspace or an online code editor work space, etc.) and it cannot be automatically downloaded to be generated here. Please access the classroom with your account and manually download the workspace to your local machine. Note that for some courses, Udacity upload the workspace files onto https://github.com/udacity, so you may be able to download them there.
Workspace Information:
- Default file path:
- Workspace type: sql-evaluator
- Opened files (when workspace is loaded): n/a
SOLUTION:
- The **ON** statement **should** always occur with the foreign key being equal to the primary key.
- **JOIN** statements allow us to pull data from multiple tables in a **SQL** database.
- You can use all of the commands we saw in the first lesson along with **JOIN** statements.
SOLUTION:
- Aliasing is common to shorten table names when we start **JOIN**ing multiple tables together.